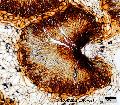
Caryoteae - Caryota
Caryoteae Drude.
informative descriptor
- general stem pattern (ex-von Mohl's classification) : Mauritia-Type
- shape of fibrous part in transverse section : Sagittata ; Reniforma to Cordata - Complanata
- cortex : very thin
- superficial protective layer (sub-epidermal) : permanent epidermis ; suberization and sclerosis of the existing ground parenchyma
- tangential elongation and anticlinal divisions of subcortical parenchyma cells : present ; absent
- fibrous bundles in central cylinder : absent
- fibrous part adjacent to the xylem : absent
- little fibrous vascular bundles (bridges) : absent (poorly developed)
- number of phloem strand : one strand throughout the central cylinder
- radial elongation of the fibrous part (in subcortical zone) : absent
- radiating parenchyma : present ; absent
- ground parenchyma of the central cylinder : rod-like cells (length > 200 µm; length / width > (3)–5) and more or less regular and large meshwork (lacunae > 250 µm) ; huge cells (∅ > 150 µm) [potential few and irregular lacunae] ; appendicular parenchyma connecting fvb
- ground parenchyma sustained growth : present (Type B)
- phytoliths : trapeziform to rondel (ex hat shaped) ; combined
- number of wide metaxylem element per fibrous vascular bundle : mostly 1 ; 1 in the the subcortical zone and the zone of transition AND 2 in the central zone
- tabular parenchyma : absent
- end wall slope : oblique ; slightly oblique
- specialisation value : 1 to ≤ 2 vessel-parenchyma pits">[2] multiple perforation plates with "narrow" perforations that span >1 to ≤ 2 vessel-parenchyma pits ; 2 to ≤ 5 vessel-parenchyma pits">[3] multiple perforation plates with "medium size" perforations that span >2 to ≤ 5 vessel-parenchyma pits ; 5 vessel-parenchyma pits, or with ≤ 3 bars">[4] multiple perforation plates with "wide" perforations that span >5 vessel-parenchyma pits, or with ≤ 3 bars ; [5] mixture of multiples perforation plates (as in #4) and simple perforation plates
- multicellular epidermal hair : present
- epidermal cells : cone shaped
- wide metaxylem element : present
- fibrous part centrifugal differentiation : present
- metaphloem sieve plate : compound
- phytoliths distribution in central cylinder : largely restricted to the fvb of the subcortical zone in contact with the cortex
- identification within "subfamily" or "tribe" : in all palm family ; subfamily Coryphoideae ; without Arecoideae
cortex
central cylinder
- fibrous bundles in central cylinder : absent
- shape of fibrous part in transverse section : Sagittata ; Reniforma to Cordata - Complanata
- little fibrous vascular bundles (bridges) : absent (poorly developed)
- radiating parenchyma : present ; absent
- tabular parenchyma : absent
- paravascular parenchyma : developed
- ground parenchyma of the central cylinder : rod-like cells (length > 200 µm; length / width > (3)–5) and more or less regular and large meshwork (lacunae > 250 µm) ; huge cells (∅ > 150 µm) [potential few and irregular lacunae] ; appendicular parenchyma connecting fvb
- ground parenchyma sustained growth : present (Type B)
- superficial protective layer (sub-epidermal) : permanent epidermis ; suberization and sclerosis of the existing ground parenchyma
- general stem pattern (ex-von Mohl's classification) : Mauritia-Type
- median sinus : rounded ; angular
- auricular lobe : rounded
- auricular sinus : angular ; absent only in the central zone
- vascular zone position : excluded from the auricular lobes only in the central zone
- fibrous part adjacent to the xylem : absent
- number of wide metaxylem element per fibrous vascular bundle : mostly 1 ; 1 in the the subcortical zone and the zone of transition AND 2 in the central zone
- number of phloem strand : one strand throughout the central cylinder
- radial elongation of the fibrous part (in subcortical zone) : absent
- phytoliths : trapeziform to rondel (ex hat shaped) ; combined
- Tomlinson's end wall type : moderately specialized
- end wall slope : oblique ; slightly oblique
- range of slope index (min_m_max) : 3 – 3,76 – 4,33
- specialisation value : 1 to ≤ 2 vessel-parenchyma pits">[2] multiple perforation plates with "narrow" perforations that span >1 to ≤ 2 vessel-parenchyma pits ; 2 to ≤ 5 vessel-parenchyma pits">[3] multiple perforation plates with "medium size" perforations that span >2 to ≤ 5 vessel-parenchyma pits ; 5 vessel-parenchyma pits, or with ≤ 3 bars">[4] multiple perforation plates with "wide" perforations that span >5 vessel-parenchyma pits, or with ≤ 3 bars ; [5] mixture of multiples perforation plates (as in #4) and simple perforation plates
- fibrous part centrifugal differentiation : present
- wide metaxylem element : present
- tangential elongation and anticlinal divisions of subcortical parenchyma cells : present ; absent
- metaphloem sieve plate : compound
- phytoliths distribution in central cylinder : largely restricted to the fvb of the subcortical zone in contact with the cortex
fibrous vascular bundle
- shape of fibrous part in transverse section : Sagittata ; Reniforma to Cordata - Complanata
- fibrous part adjacent to the xylem : absent
- number of wide metaxylem element per fibrous vascular bundle : mostly 1 ; 1 in the the subcortical zone and the zone of transition AND 2 in the central zone
- number of phloem strand : one strand throughout the central cylinder
- radial elongation of the fibrous part (in subcortical zone) : absent
- paravascular parenchyma : developed
- median sinus : rounded ; angular
- auricular lobe : rounded
- auricular sinus : angular ; absent only in the central zone
- vascular zone position : excluded from the auricular lobes only in the central zone
- tabular parenchyma : absent
- Tomlinson's end wall type : moderately specialized
- end wall slope : oblique ; slightly oblique
- range of slope index (min_m_max) : 3 – 3,76 – 4,33
- specialisation value : 1 to ≤ 2 vessel-parenchyma pits">[2] multiple perforation plates with "narrow" perforations that span >1 to ≤ 2 vessel-parenchyma pits ; 2 to ≤ 5 vessel-parenchyma pits">[3] multiple perforation plates with "medium size" perforations that span >2 to ≤ 5 vessel-parenchyma pits ; 5 vessel-parenchyma pits, or with ≤ 3 bars">[4] multiple perforation plates with "wide" perforations that span >5 vessel-parenchyma pits, or with ≤ 3 bars ; [5] mixture of multiples perforation plates (as in #4) and simple perforation plates
- metaphloem sieve plate : compound
- wide metaxylem element : present
- fibrous part centrifugal differentiation : present
- radiating parenchyma : present ; absent
ground parenchyma
- ground parenchyma of the central cylinder : rod-like cells (length > 200 µm; length / width > (3)–5) and more or less regular and large meshwork (lacunae > 250 µm) ; huge cells (∅ > 150 µm) [potential few and irregular lacunae] ; appendicular parenchyma connecting fvb
- ground parenchyma sustained growth : present (Type B)
- superficial protective layer (sub-epidermal) : permanent epidermis ; suberization and sclerosis of the existing ground parenchyma
- tangential elongation and anticlinal divisions of subcortical parenchyma cells : present ; absent